The Secrets of Eye Dissection: 4 Tips

The intricate process of eye dissection is a fascinating journey into the depths of visual perception. This delicate procedure, often employed in research and medical contexts, provides an in-depth understanding of the eye's intricate structure and function. While it may seem daunting at first, with the right approach and a few key tips, eye dissection can be a rewarding and enlightening experience. In this article, we will uncover the secrets of eye dissection, offering a comprehensive guide to enhance your skills and knowledge.
Understanding the Eye: A Complex Organ
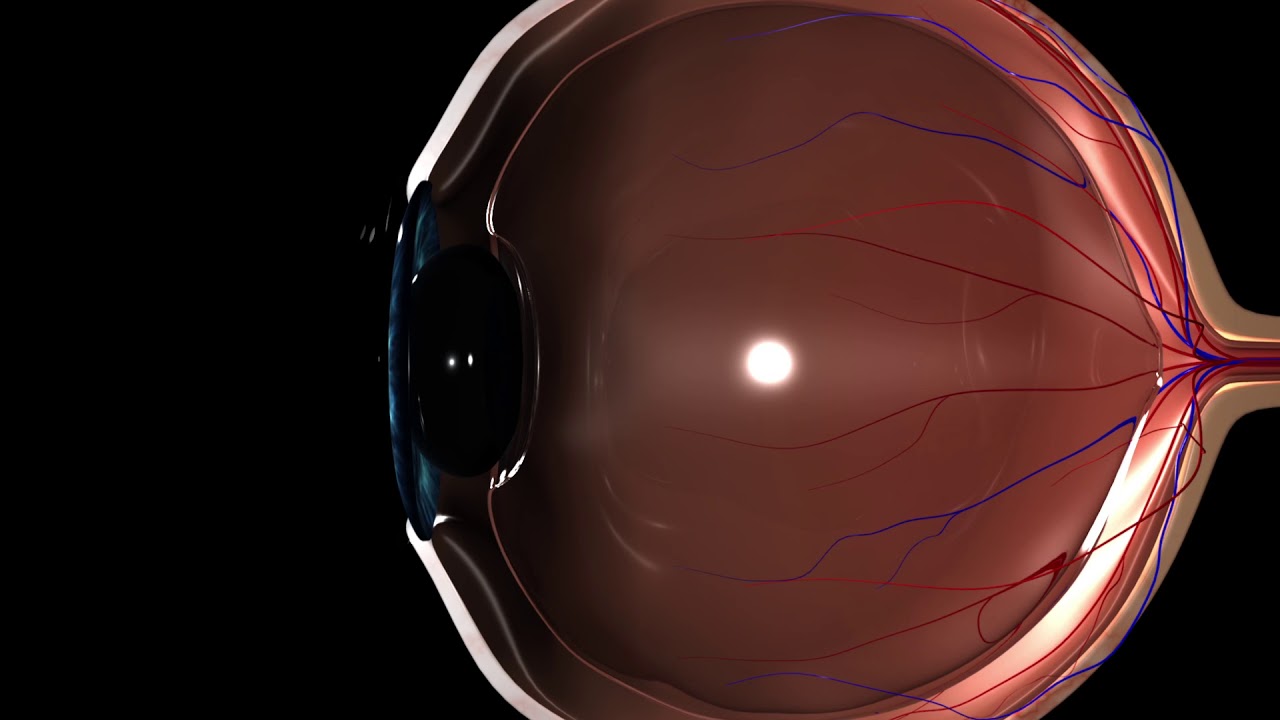
The human eye is a marvel of nature, a sophisticated optical system that allows us to perceive the world around us. It is composed of various specialized structures, each with a unique role in the process of vision. From the transparent cornea at the front, which provides the initial refraction of light, to the intricate network of blood vessels and nerves in the retina at the back, every component is essential for proper visual function.
Eye dissection allows researchers and medical professionals to study these structures in detail, aiding in the development of treatments for various eye conditions and diseases. It also provides a unique educational experience, offering a hands-on approach to understanding the complex mechanisms of vision.
Tips for a Successful Eye Dissection

Eye dissection, while challenging, can be mastered with the right techniques and a systematic approach. Here are four essential tips to enhance your eye dissection skills:
1. Master the Anatomy
Before attempting an eye dissection, a solid understanding of eye anatomy is crucial. Familiarize yourself with the various structures, such as the cornea, iris, lens, retina, and optic nerve. Knowing the location and function of each part will guide your dissection and help you identify anomalies or areas of interest.
| Eye Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Cornea | Refracts light, providing the initial focus for vision. |
| Iris | Controls the size of the pupil, regulating the amount of light entering the eye. |
| Lens | Further focuses light onto the retina, providing sharp images. |
| Retina | Contains photoreceptor cells that convert light into electrical signals. |
| Optic Nerve | Transmits visual information from the retina to the brain for processing. |

2. Choose the Right Tools
Having the appropriate tools is essential for a precise and safe eye dissection. Ensure you have a high-quality dissection kit, including sharp scalpels, fine-tipped forceps, and micro-scissors. These instruments should be sterilized and well-maintained to ensure a clean and efficient procedure. Additionally, consider using a binocular microscope to provide a clear and magnified view of the intricate structures within the eye.
3. Maintain a Sterile Environment
Sterility is crucial when working with biological samples like eyes. Ensure your work area is clean and free from contaminants. Wear personal protective equipment, including gloves and a lab coat, to prevent the spread of bacteria and other pathogens. Regularly sterilize your instruments and work surfaces to maintain a safe and controlled environment during the dissection process.
4. Take a Systematic Approach
Eye dissection is a delicate process that requires a systematic approach. Start by making a small incision in the cornea, using gentle pressure to avoid damaging the delicate structures within. Carefully peel back the layers of the eye, one by one, to expose the internal structures. Take your time and be meticulous, ensuring you do not damage or distort the natural shape of the eye. As you progress, use your understanding of anatomy to identify and label the various components, enhancing your knowledge and providing a more informative dissection experience.
The Rewards of Eye Dissection
Eye dissection offers a unique opportunity to gain a deeper understanding of the visual system. By following these tips and adopting a systematic approach, you can enhance your skills and knowledge, contributing to the advancement of eye research and medical treatments. Whether you are a student, a researcher, or a medical professional, eye dissection is a valuable tool for exploring the complexities of vision and the intricate world within the human eye.
How often should eye dissections be performed for research purposes?
+The frequency of eye dissections for research depends on the specific study and its objectives. Some research projects may require multiple dissections over a short period to gather data quickly, while others may have a longer-term focus, requiring dissections at various stages of a study. The timing and frequency of dissections are carefully planned to align with research goals and ethical considerations.
Are there any ethical considerations for eye dissections in medical research?
+Absolutely. Ethical considerations are paramount in medical research, including eye dissections. Researchers must ensure that all procedures adhere to strict ethical guidelines, prioritizing the welfare of participants and patients. Informed consent is a critical aspect, ensuring that individuals fully understand the purpose and potential risks of the dissection before participating.
Can eye dissections be performed on living subjects?
+No, eye dissections are typically performed on cadaveric eyes or animal models. Dissection on living subjects is not only ethically questionable but also impractical due to the potential for harm and the need for anesthesia. Researchers use alternative methods, such as non-invasive imaging techniques, to study the living eye.



