How Is Fast Fashion Bad For The Environment

The fashion industry, known for its rapid production cycles and ever-changing trends, has given rise to the phenomenon of fast fashion. While fast fashion has revolutionized the way we consume clothing, offering affordable and trendy options, it has also become a significant contributor to environmental degradation. The environmental impact of fast fashion is a growing concern, and understanding its detrimental effects is crucial for making informed choices and fostering a more sustainable future.
The Environmental Impact of Fast Fashion

Fast fashion’s negative impact on the environment is multi-faceted and far-reaching. From the moment the raw materials are sourced to the final disposal of garments, each stage of the fashion supply chain leaves an ecological footprint.
1. Resource Intensive Production
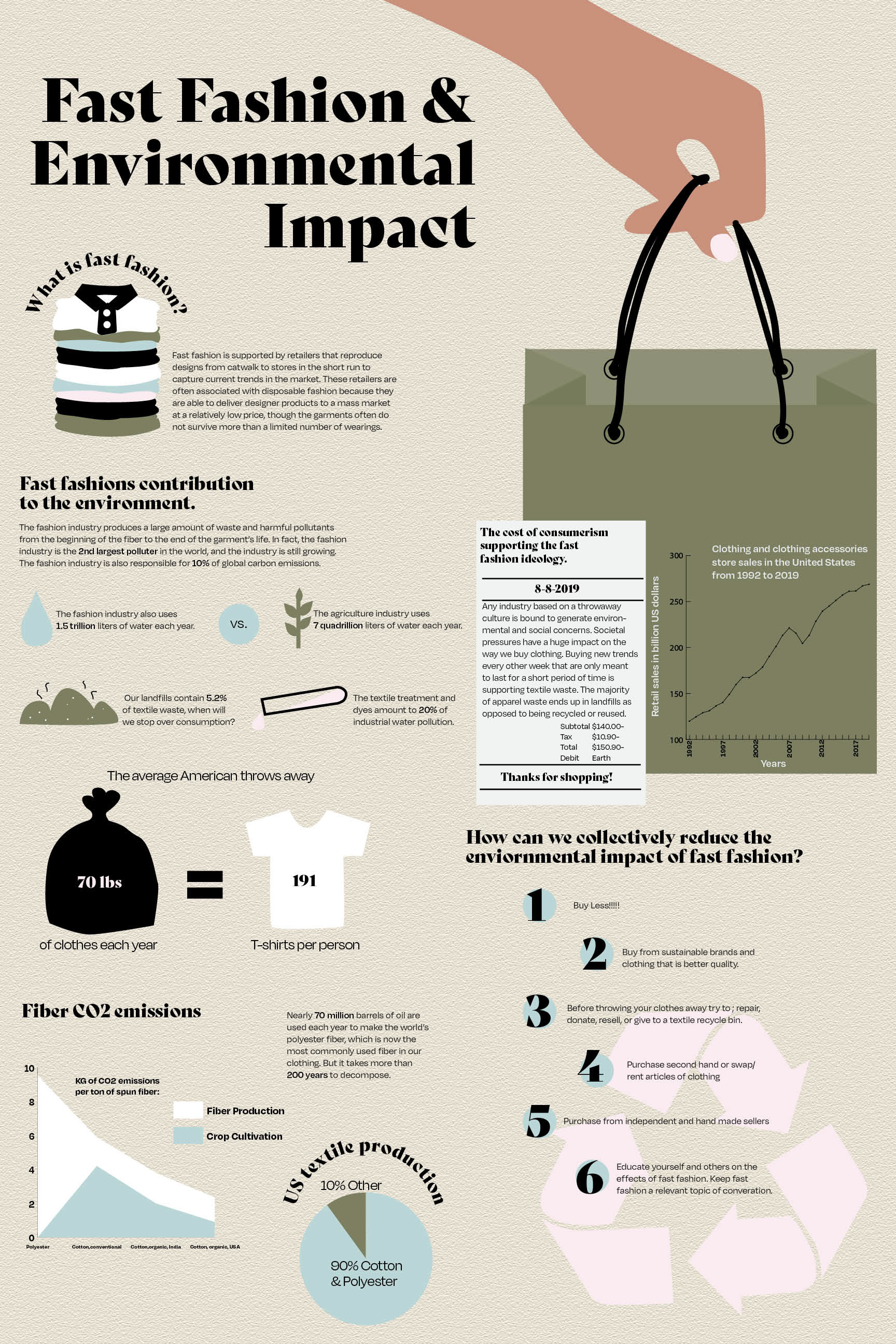
The production process in fast fashion is resource-intensive, demanding vast amounts of water, energy, and raw materials. For instance, cotton, a popular fabric in the industry, requires substantial water for irrigation. According to the Water Footprint Network, it takes approximately 2,700 liters of water to produce enough cotton for a single t-shirt.
Furthermore, the use of synthetic fibers, such as polyester and nylon, has increased in fast fashion due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of production. However, these fibers are derived from fossil fuels, contributing to the fashion industry's carbon footprint. The production of polyester, in particular, emits significant greenhouse gases, exacerbating climate change.
2. Chemical Pollution
The use of harmful chemicals in the production process is another major environmental concern. Dyes, finishes, and other chemical treatments are often used to create the desired colors, textures, and effects on garments. These chemicals, if not properly managed, can pollute water sources, harm aquatic life, and even contaminate soil, leading to long-term environmental damage.
In addition, the improper disposal of these chemicals can have severe health implications for communities living near textile factories. Workers in these factories are often exposed to hazardous substances, leading to various health issues.
3. Excessive Waste Generation
Fast fashion’s focus on disposable, trend-based clothing has led to a massive increase in textile waste. The average lifespan of a garment has decreased significantly, with many items being worn only a few times before being discarded. This rapid turnover results in a substantial amount of waste ending up in landfills, where it can take decades to decompose.
Moreover, the synthetic fibers used in fast fashion garments do not biodegrade easily. Instead, they break down into microplastics, which can enter our waterways and food chains, posing risks to both human and environmental health.
| Environmental Impact | Real Statistics |
|---|---|
| Water Consumption for Cotton Production | 2,700 liters per t-shirt |
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Polyester Production | Over 706 million metric tons of CO2 equivalent per year |
| Textile Waste Generated Annually | Over 92 million tons globally |
The Way Forward: Sustainable Alternatives

While the environmental challenges posed by fast fashion are significant, there is a growing movement towards more sustainable practices. Consumers, designers, and manufacturers are recognizing the need for change and adopting eco-friendly alternatives.
1. Eco-Friendly Materials
One of the key strategies to mitigate the environmental impact of fast fashion is the use of sustainable materials. Organic cotton, for instance, is grown without the use of harmful pesticides and fertilizers, reducing water pollution and promoting healthier ecosystems. Similarly, natural fibers like linen and hemp require less water and energy to produce, making them more environmentally friendly alternatives.
In addition, innovative materials like recycled polyester and plant-based fabrics are gaining popularity. Recycled polyester, derived from post-consumer waste like plastic bottles, reduces the demand for virgin petroleum resources and helps divert waste from landfills.
2. Sustainable Production Practices
Implementing sustainable production practices is another crucial step towards a greener fashion industry. This includes reducing water and energy consumption during manufacturing, utilizing renewable energy sources, and adopting closed-loop systems where possible. Closed-loop systems aim to minimize waste by reusing or recycling materials at the end of a product’s life cycle.
Furthermore, the adoption of digital technologies, such as 3D design and printing, can reduce the need for physical prototypes and samples, thereby decreasing waste and saving resources.
3. Circular Fashion and Extended Lifespan
Promoting circular fashion and extending the lifespan of garments is essential to combating fast fashion’s environmental footprint. Circular fashion focuses on creating a closed-loop system where products are designed to be reused, repaired, or recycled, reducing the need for constant production and disposal.
Encouraging consumers to repair and repurpose their garments, as well as supporting second-hand and rental markets, can significantly reduce waste and promote a more sustainable approach to fashion consumption.
| Sustainable Alternative | Environmental Benefit |
|---|---|
| Organic Cotton | Reduces water pollution and promotes healthier ecosystems |
| Recycled Polyester | Decreases demand for virgin petroleum resources and diverts waste from landfills |
| 3D Design and Printing | Reduces waste and saves resources by minimizing physical prototypes |
Conclusion: A Call for Conscious Consumption
The environmental impact of fast fashion is a complex issue that requires collective action. Consumers, manufacturers, and policymakers all have a role to play in fostering a more sustainable fashion industry.
By making conscious choices, such as supporting brands committed to sustainability, opting for second-hand or rental services, and embracing a more minimalist wardrobe, individuals can contribute to reducing the environmental footprint of the fashion industry. Additionally, advocating for stricter environmental regulations and supporting initiatives that promote sustainable practices can further drive positive change.
In conclusion, while fast fashion has its allure, its detrimental impact on the environment cannot be ignored. By embracing sustainable alternatives and adopting a more mindful approach to fashion consumption, we can work towards a greener and more responsible future for the industry.
How does fast fashion contribute to climate change?
+Fast fashion contributes to climate change through its high carbon footprint. The production of synthetic fibers, transportation of garments, and energy-intensive manufacturing processes all emit significant greenhouse gases, leading to global warming.
What are some sustainable materials used in fashion?
+Sustainable materials in fashion include organic cotton, linen, hemp, and recycled polyester. These materials are environmentally friendly, reducing water consumption, chemical pollution, and waste generation.
How can consumers reduce their environmental impact in fashion choices?
+Consumers can reduce their environmental impact by supporting sustainable brands, opting for second-hand or rental services, embracing a minimalist wardrobe, and advocating for sustainable practices in the industry.



