Laboratory Safety
Laboratory safety is a critical aspect of any scientific or research endeavor. It encompasses a wide range of practices and protocols aimed at protecting personnel, ensuring the integrity of experiments, and maintaining a safe working environment. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of laboratory safety, exploring its importance, key principles, and best practices. By understanding and implementing these measures, scientists, researchers, and laboratory personnel can create a secure and productive workspace.
Understanding the Significance of Laboratory Safety

Laboratory safety is not merely a set of rules to be followed; it is a fundamental pillar that underpins the success and integrity of scientific research. The significance of laboratory safety becomes evident when we consider the potential hazards and risks inherent in various laboratory environments. From handling hazardous chemicals and biological agents to working with sophisticated equipment, the laboratory setting presents a unique set of challenges.
Ensuring laboratory safety is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it safeguards the well-being of laboratory personnel. Accidents, injuries, and even fatalities can occur if proper safety measures are not in place. By implementing rigorous safety protocols, laboratories can minimize the risk of harm to their workforce, fostering a culture of care and responsibility.
Secondly, laboratory safety is crucial for maintaining the integrity of scientific research. Contamination, errors, and unintended outcomes can compromise the validity and reproducibility of experiments. By adhering to strict safety guidelines, researchers can ensure the accuracy and reliability of their findings, contributing to the advancement of knowledge in their respective fields.
Key Principles of Laboratory Safety

Laboratory safety is built upon a foundation of key principles that guide the practices and behaviors of laboratory personnel. These principles serve as a roadmap for creating and maintaining a safe working environment.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
One of the cornerstones of laboratory safety is the use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). PPE includes a range of protective gear designed to shield laboratory workers from potential hazards. This can include items such as lab coats, gloves, safety goggles, respirators, and closed-toe shoes. By wearing appropriate PPE, individuals can reduce their exposure to chemical spills, biological contaminants, and other workplace hazards.
The selection of PPE should be based on the specific risks associated with each laboratory task. For instance, when working with corrosive chemicals, acid-resistant gloves and face shields may be necessary. On the other hand, when handling biological samples, disposable gloves and lab coats can provide adequate protection. It is the responsibility of laboratory supervisors and personnel to ensure that the appropriate PPE is readily available and used consistently.
Hazard Identification and Assessment
Before any laboratory work commences, it is crucial to identify and assess potential hazards. This process involves a thorough evaluation of the substances, equipment, and procedures involved in the experiment. By understanding the inherent risks, laboratory personnel can develop appropriate safety measures and contingency plans.
Hazard identification and assessment often involve the creation of detailed laboratory protocols and standard operating procedures (SOPs). These documents outline the step-by-step procedures for conducting experiments, including the handling of hazardous materials, the use of specialized equipment, and the implementation of safety protocols. By having clear and well-defined SOPs, laboratory personnel can minimize the likelihood of accidents and ensure a consistent approach to safety.
Emergency Preparedness
Accidents and emergencies can occur even in the most well-prepared laboratories. Therefore, it is essential to have comprehensive emergency response plans in place. These plans should outline the procedures to follow in the event of fires, chemical spills, injuries, or other unforeseen incidents.
Laboratory personnel should be trained in basic first aid and emergency response techniques. This includes knowing how to administer CPR, use fire extinguishers, and handle hazardous material spills. Regular drills and simulations can help reinforce these skills and ensure that everyone is prepared to respond effectively in a real-life emergency situation.
Proper Waste Disposal
The safe disposal of laboratory waste is a critical aspect of laboratory safety. Improper waste management can lead to environmental contamination and pose risks to public health. It is essential to have clear guidelines and protocols for the segregation, collection, and disposal of different types of laboratory waste.
Laboratory waste can be classified into various categories, including chemical waste, biological waste, radioactive waste, and sharps (needles, scalpels, etc.). Each category requires specific handling and disposal methods. For instance, chemical waste may need to be neutralized or treated before disposal, while biological waste must be sterilized or incinerated.
Best Practices for Laboratory Safety
In addition to adhering to the key principles of laboratory safety, there are several best practices that can further enhance the safety culture within a laboratory setting.
Training and Education
Investing in comprehensive training and education programs is vital for fostering a safety-conscious culture. Laboratory personnel should receive training on safety protocols, hazard identification, and emergency response procedures. This training should be ongoing and tailored to the specific needs of each laboratory.
In addition to formal training sessions, regular safety meetings and discussions can help keep safety at the forefront of everyone's minds. These meetings provide an opportunity to review recent incidents, discuss emerging safety concerns, and share best practices. By encouraging open communication and continuous learning, laboratories can create a collaborative and safety-oriented environment.
Regular Equipment Maintenance
The proper maintenance and calibration of laboratory equipment are essential for ensuring its safe and reliable operation. Faulty or malfunctioning equipment can pose significant risks to laboratory personnel and the integrity of experiments.
Laboratories should have established maintenance schedules for all critical equipment. This includes regular inspections, calibration checks, and timely repairs. By maintaining equipment in optimal condition, laboratories can reduce the likelihood of equipment-related accidents and ensure accurate and consistent experimental results.
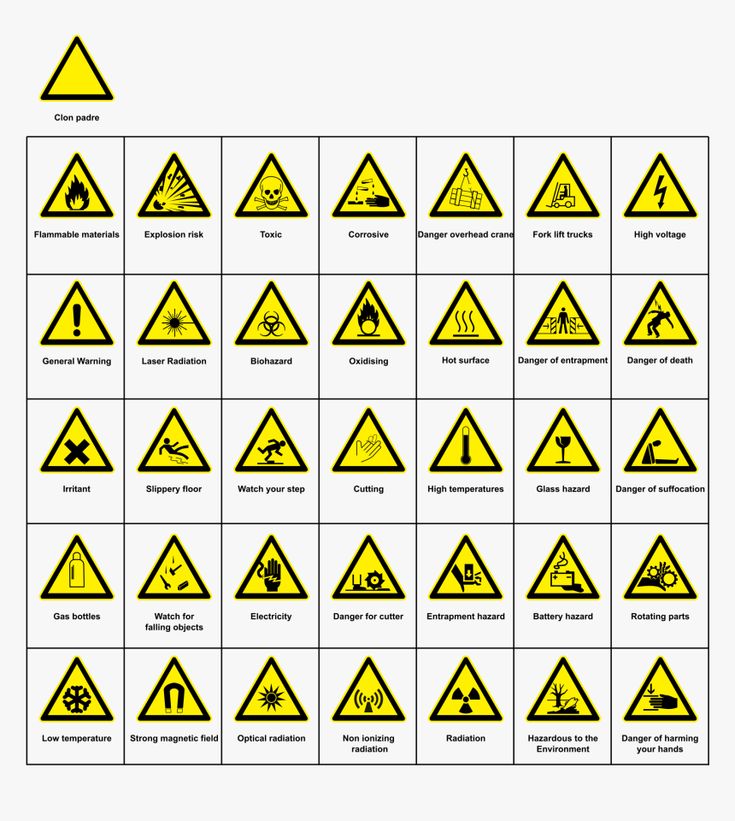
Clear Signage and Communication
Effective communication is key to maintaining laboratory safety. Clear and concise signage should be displayed throughout the laboratory, indicating potential hazards, emergency procedures, and the location of safety equipment.
In addition to signage, laboratories should encourage open communication among personnel. This includes reporting near-miss incidents, sharing safety concerns, and providing feedback on safety protocols. By creating an environment where safety is a shared responsibility, laboratories can identify and address potential issues before they escalate.
Safety Audits and Continuous Improvement
Laboratories should conduct regular safety audits to assess their adherence to safety protocols and identify areas for improvement. These audits can be conducted internally or by external safety consultants.
During a safety audit, various aspects of laboratory operations are examined, including the storage and handling of hazardous materials, the implementation of safety protocols, and the effectiveness of emergency response plans. Based on the findings of the audit, laboratories can develop action plans to address any identified gaps or weaknesses.
Case Studies: Real-World Laboratory Safety Scenarios
Understanding the practical application of laboratory safety principles is crucial for implementing effective measures. Let’s explore a few case studies that highlight the importance of laboratory safety and the potential consequences of overlooking these critical practices.
Chemical Spill Incident
In a research laboratory specializing in organic chemistry, a graduate student was working with a highly corrosive chemical. Despite being aware of the potential hazards, the student failed to wear the appropriate PPE, including acid-resistant gloves and a face shield.
While transferring the chemical from one container to another, a small amount spilled onto the student's hand. The corrosive nature of the chemical resulted in severe burns and required immediate medical attention. This incident served as a stark reminder of the importance of adhering to safety protocols and using appropriate PPE.
Biological Contamination
A microbiology laboratory was conducting experiments involving pathogenic bacteria. The laboratory had strict protocols in place for the handling and disposal of biological samples. However, a lapse in concentration led to a technician accidentally contaminating their lab coat with a sample of the pathogen.
The technician, unaware of the contamination, proceeded to handle other laboratory equipment and samples. This led to the potential spread of the pathogen within the laboratory. Fortunately, the laboratory's emergency response plan was activated, and the situation was quickly contained. The incident highlighted the need for vigilance and adherence to safety protocols, even in seemingly routine tasks.
Equipment Malfunction
In a physics laboratory, a sophisticated piece of equipment, known for its precision and accuracy, malfunctioned during a critical experiment. The equipment, which had not been calibrated in several months, provided inaccurate readings, leading to flawed experimental results.
The researchers, unaware of the equipment's malfunction, continued to rely on the data, only to discover the error weeks later. This incident emphasized the importance of regular equipment maintenance and calibration, ensuring the reliability and integrity of experimental data.
The Future of Laboratory Safety

As scientific research and technological advancements continue to evolve, so too must laboratory safety practices. The future of laboratory safety lies in staying abreast of emerging technologies, understanding new hazards, and adapting safety protocols accordingly.
One area of focus is the development of advanced safety equipment and technologies. From smart PPE that provides real-time hazard detection to automated waste management systems, these innovations aim to enhance safety and efficiency in laboratory environments. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning can play a crucial role in predicting and mitigating potential hazards.
Furthermore, the future of laboratory safety is intertwined with the promotion of a safety-oriented culture. This involves fostering a sense of collective responsibility among laboratory personnel, encouraging open dialogue, and continuously refining safety protocols based on real-world experiences and feedback.
| Key Takeaway | Actionable Tip |
|---|---|
| Laboratory safety is essential for protecting personnel and maintaining research integrity. | Conduct regular safety audits and encourage open communication to identify and address safety concerns. |
| Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is crucial for minimizing exposure to hazards. | Ensure that laboratory personnel are trained on the proper use and selection of PPE based on task-specific risks. |
| Hazard identification and assessment are vital for developing effective safety protocols. | Create detailed laboratory protocols and SOPs to guide personnel through safe experimental procedures. |

What are some common hazards encountered in laboratories?
+
Laboratories may encounter a range of hazards, including chemical spills, biological contamination, radiation exposure, electrical hazards, and equipment malfunctions. Proper training and safety protocols are essential to mitigate these risks.
How often should laboratory equipment be maintained and calibrated?
+
The frequency of equipment maintenance and calibration depends on the type of equipment and its usage. As a general guideline, critical equipment should be inspected and calibrated at least annually, while less critical equipment may require maintenance on a bi-annual or tri-annual basis.
What are some best practices for laboratory waste management?
+
Effective laboratory waste management involves proper segregation, collection, and disposal of different types of waste. This includes having dedicated containers for chemical, biological, and radioactive waste, as well as implementing a clear labeling system to identify the contents of each waste container.



