What Is A Lock Out Tag Out
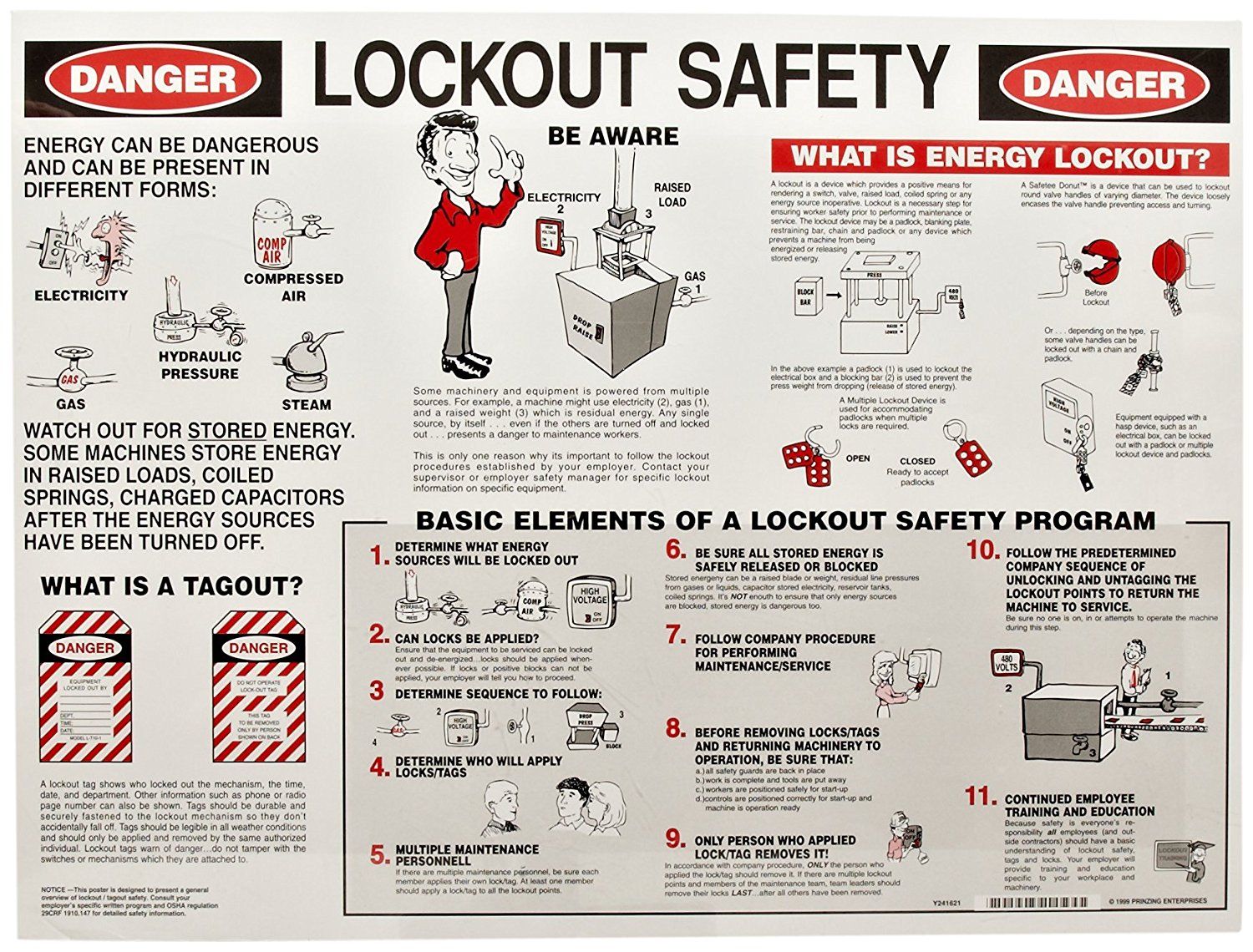
In the realm of industrial safety, the term "Lock Out Tag Out" (LOTO) often arises as a critical procedure, designed to safeguard workers from the unexpected activation or energization of machinery and equipment during maintenance or servicing activities. This comprehensive process aims to mitigate the risk of accidents, injuries, or even fatalities by ensuring that machines remain in a safe, de-energized state until work is completed.
The importance of LOTO cannot be overstated, especially in industries where the operation of heavy machinery and equipment is prevalent. Its implementation is a cornerstone of safety protocols, aimed at preventing the all-too-common accidents that can occur when machines unexpectedly start up or release stored energy during maintenance.
The Basics of Lock Out Tag Out
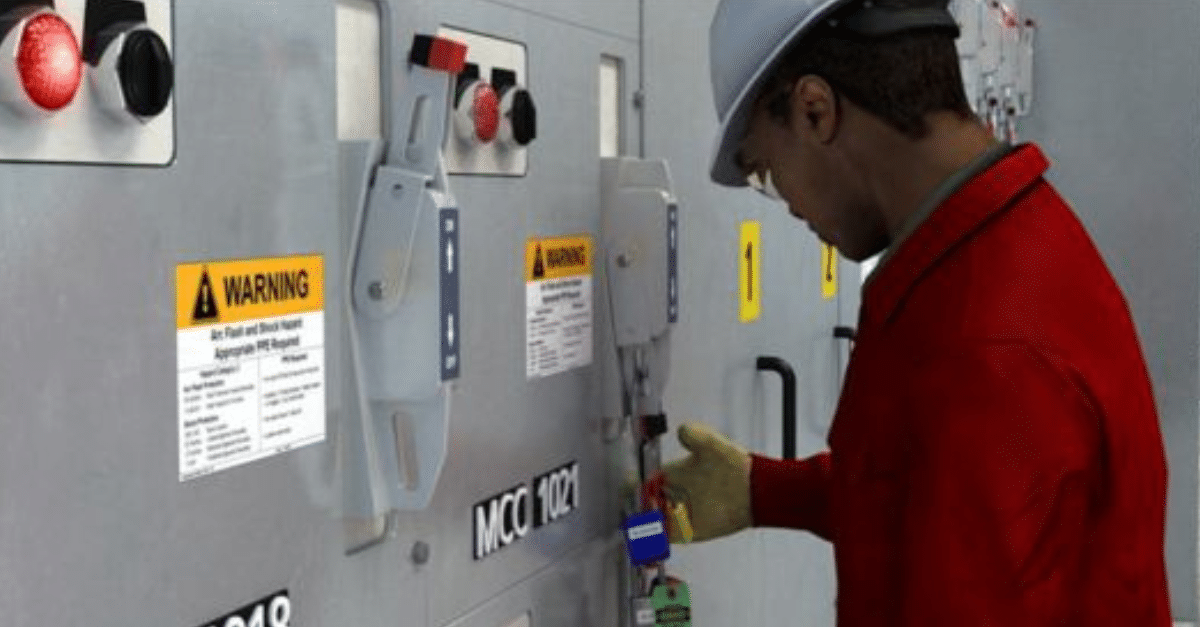

Lock Out Tag Out is a systematic procedure that involves the physical locking of energy-isolating devices and the placement of tags to indicate that the equipment is locked out and should not be operated.
The primary objective of LOTO is to create a safe work environment by ensuring that equipment and machinery cannot be started up or activated inadvertently. This process is typically followed when workers need to perform maintenance, repairs, or servicing tasks on equipment that could pose a hazard if it were to start up unexpectedly.
The Process of Lock Out Tag Out
The LOTO process typically involves several key steps, each of which is critical to ensuring a safe work environment:
- Notification and Preparation: Before any maintenance or servicing work can begin, the relevant personnel must be notified about the upcoming LOTO procedure. This includes the workers who will be performing the maintenance as well as those who operate the equipment regularly. Preparation includes gathering the necessary tools, locks, and tags, as well as ensuring that the work area is clear of any potential hazards.
- Equipment Isolation: The next step involves physically isolating the equipment from its energy source(s). This could mean turning off electrical power, disconnecting fuel lines, or blocking the movement of mechanical parts. The specific method of isolation will depend on the type of equipment and the energy sources it utilizes.
- Locking Out: Once the equipment is isolated, the worker performing the LOTO procedure will attach a lock to the energy-isolating device(s). This lock physically prevents the equipment from being re-energized. The worker will use a personal lock, ensuring that only they hold the key to unlock it, thus maintaining control over the equipment's status.
- Tag Out: In addition to locking out the equipment, a tag is also attached. This tag serves as a visual warning, indicating that the equipment is locked out and should not be operated. The tag typically includes information about the reason for the lockout, the date, and the name or identification of the person who initiated the LOTO procedure.
- Verification: After locking and tagging out the equipment, the worker must verify that the equipment is indeed de-energized and cannot be accidentally started. This could involve testing for the absence of electrical current, ensuring that fuel valves are shut off, or confirming that mechanical parts are secure and immobile.
- Communication: Effective communication is crucial throughout the LOTO process. All personnel who may interact with the equipment should be informed about the LOTO procedure and the reasons for it. This ensures that everyone is aware of the equipment's status and understands the importance of maintaining the lockout until work is completed.
- Release of Lockout: Once the maintenance or servicing work is completed, the LOTO procedure is reversed. The worker removes their lock and tag, verifies that the equipment is safe to operate, and then communicates this to relevant personnel. Only then can the equipment be re-energized and put back into operation.
It's important to note that the LOTO procedure is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Different types of equipment and energy sources may require unique approaches to ensure a safe lockout. As such, it's crucial for workers to be thoroughly trained in the specific LOTO procedures relevant to their workplace.
The Benefits of Lock Out Tag Out

The implementation of Lock Out Tag Out procedures offers several key benefits, which contribute to the overall safety and efficiency of industrial operations:
- Prevention of Accidents: By ensuring that equipment remains de-energized during maintenance, LOTO significantly reduces the risk of accidents. This is particularly crucial for machinery that can cause severe injuries or fatalities if activated unexpectedly.
- Enhanced Worker Safety: LOTO empowers workers to take control over the safety of their work environment. The personal lock system ensures that only authorized personnel can re-energize equipment, reducing the risk of unauthorized or accidental activation.
- Improved Communication: The LOTO procedure promotes effective communication among workers. The use of tags provides a clear visual indication of the equipment's status, ensuring that all personnel are aware of the ongoing maintenance work and the associated safety precautions.
- Compliance with Safety Regulations: Many industries are governed by strict safety regulations, and LOTO is often a mandated procedure. By implementing LOTO, businesses can ensure compliance with these regulations, avoiding potential fines or legal repercussions.
- Reduced Downtime: While LOTO procedures may seem time-consuming, they can actually contribute to reduced downtime in the long run. By preventing accidents and ensuring safe maintenance practices, LOTO minimizes the likelihood of equipment damage or worker injuries, both of which can lead to costly and time-consuming repairs or absences.
Real-World Applications of Lock Out Tag Out
Lock Out Tag Out procedures find application across a wide range of industries, each with its own unique set of challenges and safety considerations. Here are some examples of how LOTO is implemented in various sectors:
Manufacturing
In manufacturing facilities, where heavy machinery and production lines are common, LOTO is crucial for maintaining a safe work environment. Workers may need to perform maintenance on conveyors, assembly lines, or large machinery. LOTO ensures that these machines remain de-energized during maintenance, preventing accidental start-ups that could lead to serious injuries or equipment damage.
Construction
Construction sites often involve the use of powerful equipment such as cranes, bulldozers, and power tools. LOTO procedures are essential for ensuring that this equipment remains safe to work around. For instance, before performing maintenance on a crane, the operator would lock out the power source and place a tag indicating that the crane is out of service.
Energy Sector
The energy sector, including oil and gas, as well as renewable energy, presents unique challenges when it comes to safety. LOTO procedures are vital for ensuring the safe maintenance of equipment such as turbines, generators, and power transmission systems. For example, before performing maintenance on a wind turbine, the technician would lock out the power supply and tag the turbine to indicate that it is out of service.
Healthcare
Even in healthcare settings, LOTO procedures play a crucial role in ensuring patient and staff safety. For instance, medical equipment such as MRI machines or radiation therapy devices require periodic maintenance. LOTO ensures that these machines are properly de-energized and tagged, preventing accidental activation during maintenance and reducing the risk of radiation exposure.
| Industry | Example Equipment |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Assembly Lines, Conveyors, Heavy Machinery |
| Construction | Cranes, Bulldozers, Power Tools |
| Energy Sector | Turbines, Generators, Power Transmission Systems |
| Healthcare | MRI Machines, Radiation Therapy Devices |

These real-world applications highlight the versatility and importance of Lock Out Tag Out procedures across diverse industries. Regardless of the specific equipment or energy sources involved, LOTO remains a critical component of any comprehensive safety program, aimed at protecting workers and ensuring the smooth operation of industrial processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is Lock Out Tag Out important for workplace safety?
+Lock Out Tag Out (LOTO) is crucial for workplace safety as it prevents the unexpected activation or energization of machinery during maintenance, repairs, or servicing. This helps prevent accidents, injuries, and fatalities, making it a fundamental safety procedure in industries that use heavy machinery and equipment.
Who is responsible for implementing Lock Out Tag Out procedures?
+Responsibility for implementing LOTO procedures typically falls on the workers performing the maintenance or servicing work. However, it’s essential that all personnel who interact with the equipment are aware of and respect the LOTO procedure. Management and safety officers also play a role in ensuring proper training and compliance with LOTO protocols.
Are there specific guidelines or regulations for Lock Out Tag Out procedures?
+Yes, many countries and industries have specific regulations and guidelines for LOTO procedures. For example, in the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has detailed requirements outlined in its Control of Hazardous Energy (Lockout/Tagout) standards. These regulations ensure that LOTO procedures are consistently applied across industries, enhancing worker safety.



